Protecting Palms, Livelihoods, and the Environment
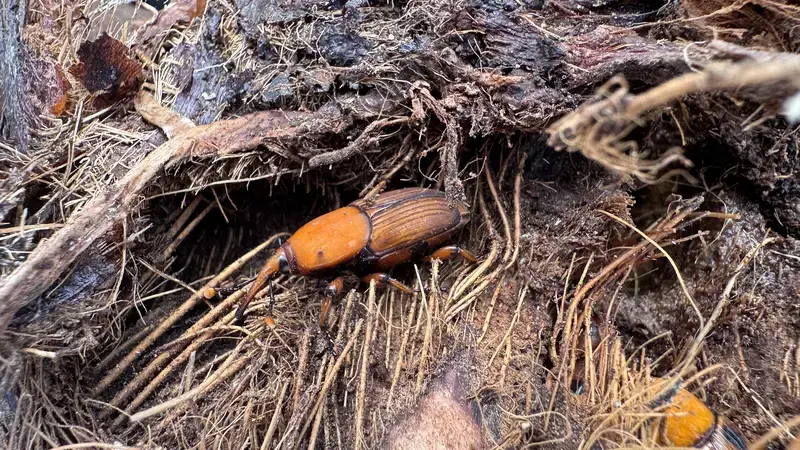
The Global Fight Against Red Palm Weevil (RPW)
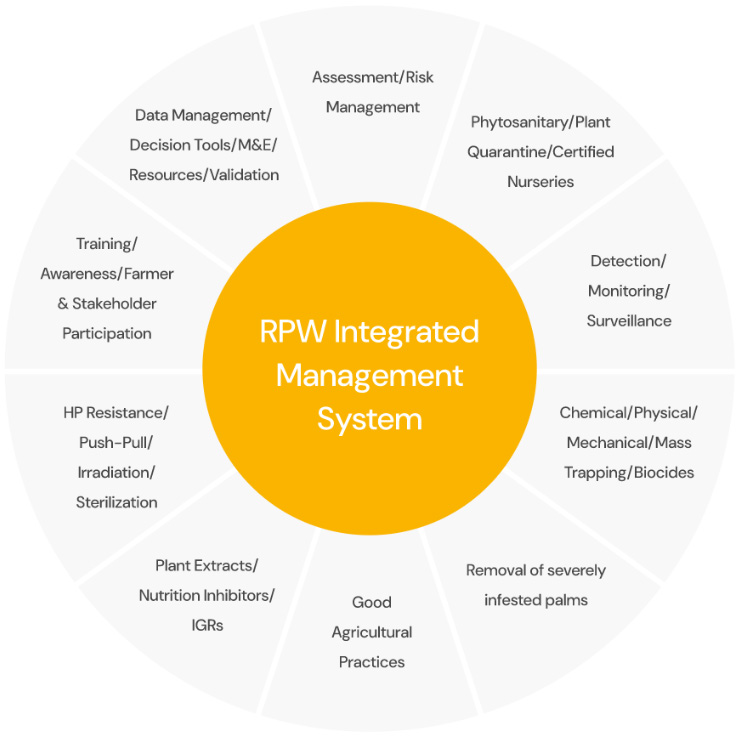
Our Solution:The C4RPWC Approach

ICARDA’s dual role as the consortium coordinator and the lead for scaling and socioeconomics is crucial for bridging scientific innovation with real-world implementation.


ICARDA’s dual role as the consortium coordinator and the lead for scaling and socioeconomics is crucial for bridging scientific innovation with real-world implementation.
Co-leads and supporting partners act as collaborators contributing complementary skills, infrastructure, and regional insights.
Private sector involvement will ensure that technology providers contribute to practical and scalable solutions.
The Five Pillars of Action
The C4RPWC program integrates five research-for-innovation workstreams to develop and scale sustainable solutions.

Biobased Solutions
Lead: International Centre for Insect Physiology and Ecology (icipe)
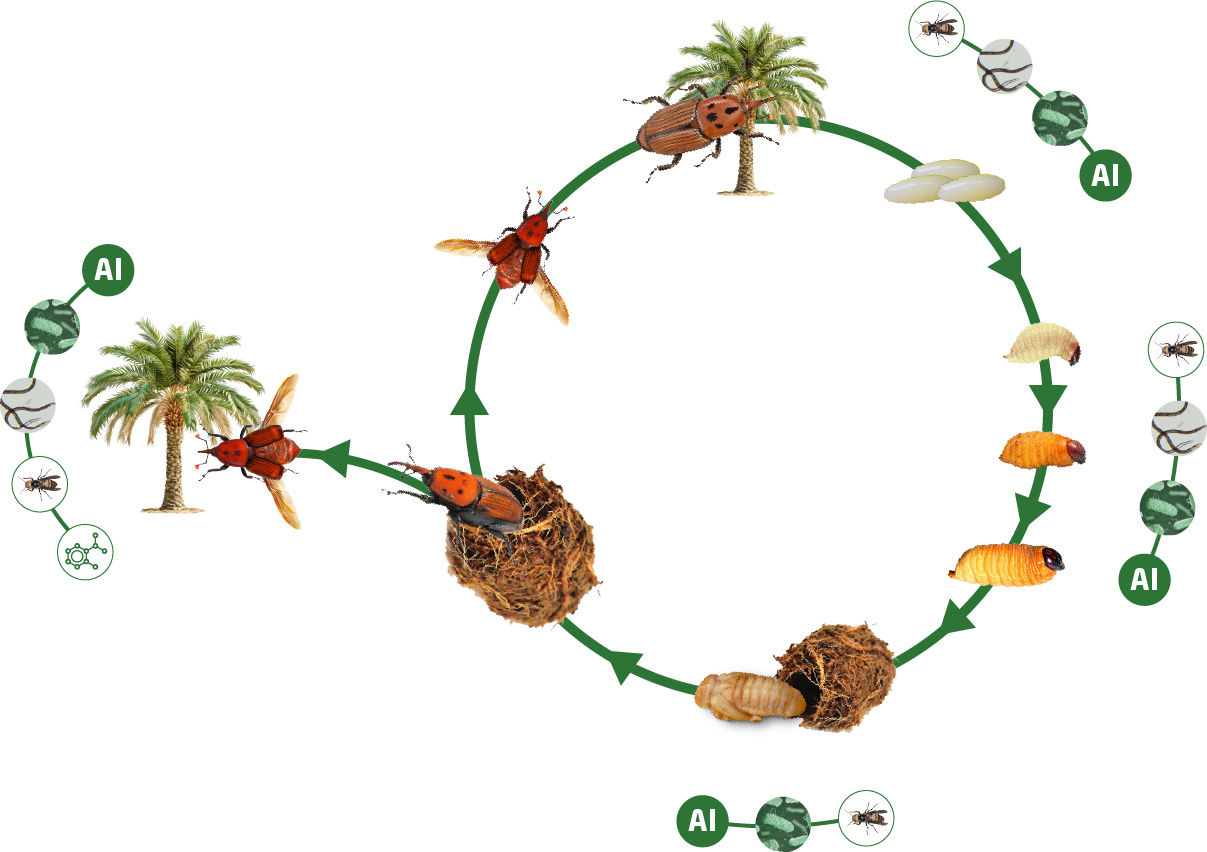
Developing eco-friendly traps, biopesticides, and natural predators to reduce RPW populations.
Digital Innovations & Big Data
Lead: International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT)
Artificial Intelligence, remote sensing, and Internet of Things sensors for early detection and outbreak prevention.


Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs)
Lead: International Center for Biosaline Agriculture (ICBA)
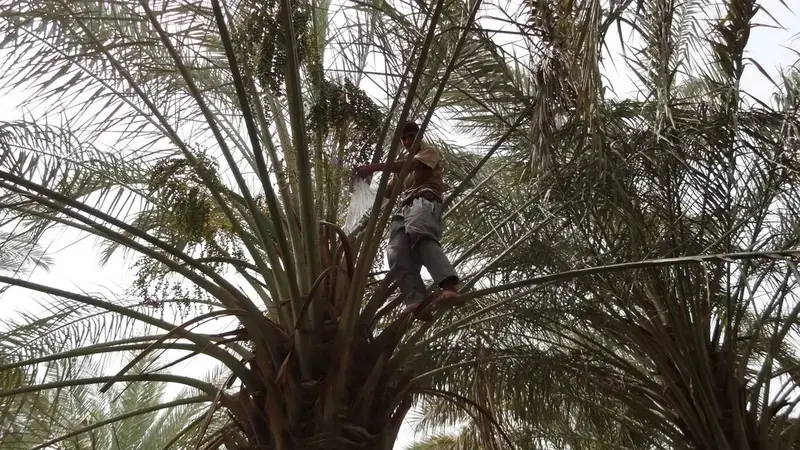
Strengthening palm health through better irrigation, certified seedlings, and pest-resistant crops.
Translating Research into Action
Lead: ICARDA
Ensuring real-world impact through scaling strategies, farmer adoption pathways, community engagement and citizen science, and economic and policy analysis for sustainable RPW management.
Roadmap to Impact
New innovations under the C4RPWC program’s five pillars of action will lead to improved ecological resistance of date palm to RPW infestations, and therefore will improve productivity of date palms in the United Arab Emirates and low- and middle-income countries. The development impact will be twofold:
- improved environmental and human health due to reduced pesticide use
- reduced losses to biotic threats on farms
Challenges
Research areas
Outputs
Facilitated by…
Provided that...
Development outcomes and impacts
Potential Benefits to LMICs
- Improved readiness for dealing with invasive species
- Demonstrating how community engagement can facilitate pest management
- Reduced pesticide costs and improved agricultural productivity
- Improved readiness for scaling up of early detection and timely warning system
- Training, awareness program, and support to extension services
- Adaptable and adoptable user-friendly and inexpensive mobile app for early detection, monitoring, and early decision for action
- Strengthening invasive species policies
Meet the Partners